L*, a* b* measurement for skin brightness and erythema, and a Mexameter® MX 16 for melanin content and hemoglobin (erythema). The instrumental measurements were performed on mid-forehead, both cheeks, neck, and on both dorsal forearms. Digital photographs were captured at baseline, 3, 6, 9, and 12 months with Canfield Scientific’s VISIA CR 2.2 booth system (Washington, DC) or VISIA CR (Los Angeles, CA) with eyes closed using standard, cross-polarized and UV fluorescence lightening modes.
Immunohistochemistry and image analysis
2 mm diameter skin biopsies were collected from a small subset of study subjects from the cheek at baseline and 12 months. At the end of 12 months, n=3 from real life study and n=6 from sunscreen study were obtained. Biopsy samples were fixed in 10% formalin, prepared into tissue sections and stained for Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), Masson’s Trichrome, Fontana Masson, and Toluidine Blue. Presence of macrophages were immunostained using CD68 antibody (pre-diluted concentration, PM033A RTU, Biocare Medical, Pacheco, CA) followed by DAB staining (DAB peroxidase substrate kit, Abcam, Cambridge, MA). Digital images were captured (DMi8 Fluorescent Microscope, Leica, Buffalo Grove, IL) and image analysis was performed blindly by two individual assessors using Image J Analysis software.
Data analysis
All statistical analyses were carried out using paired t-test to determine whether there was a change from baseline to 12 months. Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used for Investigator’s expert assessments, clinical grading of the efficacy parameters and tolerance parameters, as well as the parameters from image analysis results. The average change from baseline was calculated at each post-baseline evaluation visit. All differences were considered to be statistically significant at P<0.05 level.
L* values, ITA values (Chromameter) and melanin values (Mexameter) were calculated for each parameter for sunscreen group and real life group as mean +/-SD for 3, 6, 9, and 12 months. Change from baseline and comparison between the two groups were calculated and expressed as mean difference and the p values were calculated.
Immunohistochemistry and image analysis
2 mm diameter skin biopsies were collected from a small subset of study subjects from the cheek at baseline and 12 months. At the end of 12 months, n=3 from real life study and n=6 from sunscreen study were obtained. Biopsy samples were fixed in 10% formalin, prepared into tissue sections and stained for Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), Masson’s Trichrome, Fontana Masson, and Toluidine Blue. Presence of macrophages were immunostained using CD68 antibody (pre-diluted concentration, PM033A RTU, Biocare Medical, Pacheco, CA) followed by DAB staining (DAB peroxidase substrate kit, Abcam, Cambridge, MA). Digital images were captured (DMi8 Fluorescent Microscope, Leica, Buffalo Grove, IL) and image analysis was performed blindly by two individual assessors using Image J Analysis software.
Data analysis
All statistical analyses were carried out using paired t-test to determine whether there was a change from baseline to 12 months. Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used for Investigator’s expert assessments, clinical grading of the efficacy parameters and tolerance parameters, as well as the parameters from image analysis results. The average change from baseline was calculated at each post-baseline evaluation visit. All differences were considered to be statistically significant at P<0.05 level.
L* values, ITA values (Chromameter) and melanin values (Mexameter) were calculated for each parameter for sunscreen group and real life group as mean +/-SD for 3, 6, 9, and 12 months. Change from baseline and comparison between the two groups were calculated and expressed as mean difference and the p values were calculated.
RESULTS
Improvement on Photoaging and Dyschromia Conditions With 12-Month Daily Application Of SPF20/PPD20
Skin conditions especially skin tone and texture tend to vary based on seasonality and outdoor activities. We observed that in the real life group, a shift of color and hyperpigmented lesions towards worsening occurs in the summer with partial recovery
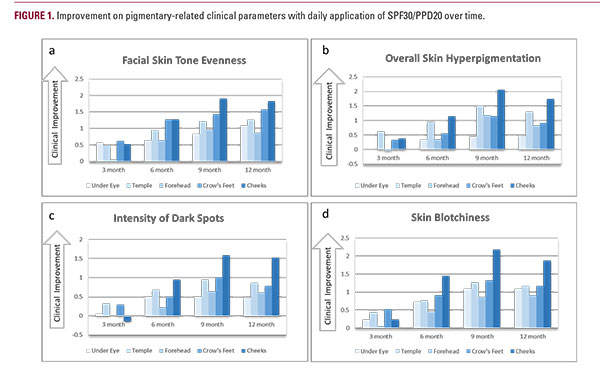
Skin conditions especially skin tone and texture tend to vary based on seasonality and outdoor activities. We observed that in the real life group, a shift of color and hyperpigmented lesions towards worsening occurs in the summer with partial recovery







