treatment period) by creating an inhospitable environment for some microbes and a boon for others, with yet unclear longterm post-treatment implications.108,109 Despite this, it should be noted these medications are all capable of (at least transiently) improving acne severity.
Systemic antibiotic therapy is the cornerstone for moderatesevere AV therapy.106 While broad-spectrum antibiotics may achieve transient improvements, they may also induce longterm CM alterations. In one longitudinal prospective study, 4 women ages 25 to 32 with recently diagnosed AV were given oral minocycline 100 mg twice daily for 4 weeks. Superficial cutaneous swabs found a 1.4-fold reduction in C. acnes counts with a trend towards C. acnes abundance recovery 8 weeks after minocycline discontinuation, but a sustained reduction in Lactobacillus spp. and Corynebacterium spp. over the same time interval.110
Isotretinoin is one of the few prescription AV therapies that consistently achieves durable response.106,111 Several studies suggest this may be due in part to modulations of the microbiome.64-66,109 CM samples post-isotretinoin therapy have found up to a 100-fold decrease in C. acnes colonies (including strains resistant to erythromycin, clindamycin, and tetracycline) 1 month after completion of 18-week isotretinoin course65 and increased diversity of other taxa.66 This CM recalibration may be a result of an isotretinoin-induced sebaceous drought that induces a microbial survival "bottleneck", which allows nonvirulent C. acnes strains to repopulate the follicles.64
Rosacea
Systemic antimicrobials have demonstrated efficacy in management of rosacea, primarily PPR.112,113 In a longitudinal cohort study of 12 PPR patients treated with doxycycline, superficial skin swabs found a significant 3.43-fold increase in Weissela confusa relative abundance (P=.008)97 and also a material change in the predominant genera with a baseline composition of Staphylococcus (28%), Cutibacterium (13%), Pseudomonas (9%), Corynebacterium (8%), Acinetobacter (7%), and Snodgrassella (6%) being replaced by Staphylococcus (22%), Stenotrophomonas (33%), Corynebacterium (8%) and Cutibacterium (7%) after 6 weeks of doxycycline 100 mg twice daily. 97 The significance, if any, of this microbiome shift is unknown.
Present Practices and Potential Paradigms
Dermatologists may consider the nature between EBD and dysbiosis akin to an interdependent positive feedback loop. However, clinically, the directional relationship between dysbiosis and EBD may be irrelevant if patients are counseled on therapeutic options with the potential to improve both anomalies. The authors note that skincare and OTC products, including cleansers and moisturizers, are a grossly underappreciated underappreciated and overlooked cornerstone in patient education that may complement prescription therapy.
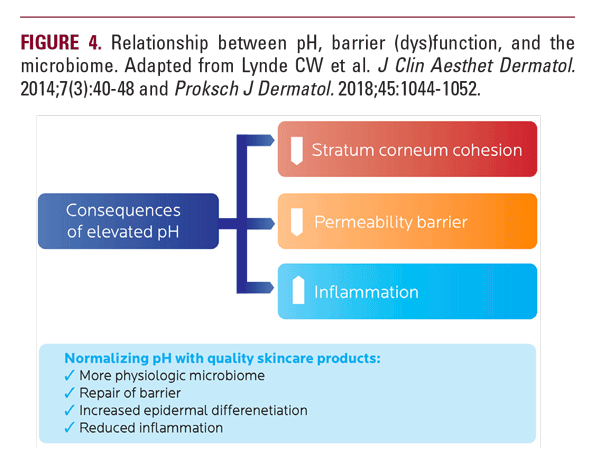
Quality moisturizers are composed of: humectants (eg, glycerin, hyaluronic acid) to attract water; occlusives that seal in moisture (eg, petrolatum); and emollients that soften and smoothen the skin.70 Effective implementation can maintain a healthy epidermal barrier, and even rescue a deficient one (Figure 4).70,115,116 For AV patients, moisturizers should also be non-comedogenic to avoid instigating additional lesions.20,21,117 Individuals with AV may also benefit from using moisturizers with ceramides to supplement their prescription regimens.23,70,117-118 Given the increased skin sensitivity seen in rosacea, moisturizers should avoid fragrances, surfactants and other potential instigators of allergic or irritant contact dermatitis, and have an acidic or physiologic pH.70
An ideal cleanser should remove debris, cosmetics, and transient bacteria without perturbing EBF or CM.70 For both AV and rosacea, cleansers should be close to physiologic skin pH (~4-6) to avoid excessive burning, stinging, and dryness and to preserve the metabolic functions, including lipid processing (Figure 4).70 Lipid-free cleansers and synthetic detergents allow for superior preservation of the skin’s natural lipids thereby decreasing irritancy.70
Therapeutic Probiotics
In addition to these essential qualities of skincare regimens, the authors note the clinical potential to augment current skincare products by utilizing pro-/pre-/postbiotics to further mend EBD and restore microbiome diversity and richness.
Probiotics are foods (eg, yogurts, fermented products such as kefir and kombucha) and topical/oral supplements that contain live microorganisms such as Nitrosomonas eutropha, Lactobacillus spp. Lactococcus spp., Streptococcus spp., and






