affected by solar elastosis. The presence of iron complexes in damaged tissues proves detrimental to wound healing since they increase local inflammation and microbial infection by supplying iron. TP1 stops the release of oxidizing iron from ferritin and also has sun-protective properties blocking lethal ultraviolet radiation damage to cultured skin keratinocytes and reducing UV-induced erythema.16,19,26 Alastin has studied the effect of their products’ tripeptide on human fibroblasts and shown elevations in gene expression for all of these important ECM modulating proteins at 48 hours (Table 1).
Finally, studies analyzing stem cell function in the keratinocytic basal layer of the epidermis revealed that treatment with TP1 increased the proliferative potential of basal keratinocytes possibly
by modulating the expression of integrins and p63.27 p63 is a putative stem cell marker of the skin, suggesting that TP1 promotes the survival of basal stem cells in the skin.27,28 Having achieved the capacity to activate, synthesize and remodel collagen
and elastin using TP1, a focus on elastin generation would supplement the picture for ideal skin remodeling.
Hexapetide (Hex-12) has the repeating amino acid sequence found in tropoelastin and the key sequence found at the binding site for the elastin protein to its cell surface receptor. Matrikines that predominantly activate elastin formation, elastokines, are amongst the most important matrikines yet described. This is because these elastin-derived peptides are chemotactic for fibroblasts
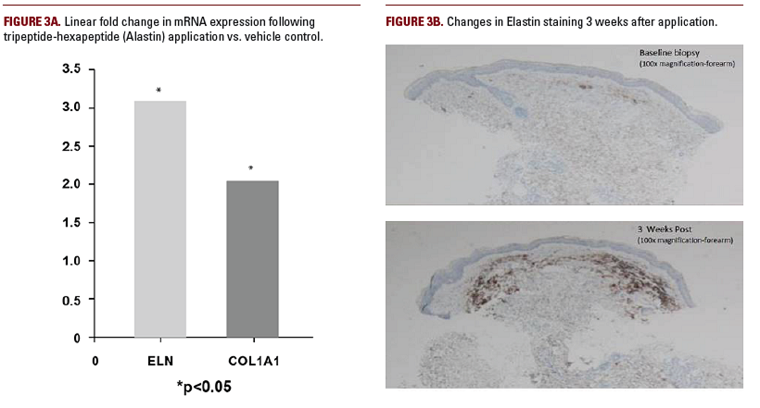
and monocytes and have the capacity to stimulate the generation of elastin (Figure 3).29,30 Hexapeptide functions as a
signal transduction cytokine, binding to Elastin Binding Protein (EBP) on the fibroblast and keratinocyte surface and stimulating
the generation of elastin. This is key as most rejuvenating procedures are designed to stimulate collagen production but regeneration of elastin is limited.
Oleuropein
Oleuropein is a polyphenol isolated from olive leaves with great interest to researchers.31,32 It demonstrates major anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting lypoxygenase activity and the production of leukotriene.32 In particular, researchers have demonstrated that oleuropein enhances proteasome activities in vitro more effectively than other known chemical
activators, possibly through conformational changes of the proteasome.31 In this regard, it decreases reactive oxygen
species (ROS), reduces the amount of oxidized proteins through increased proteasome-mediated degradation, and retains proteasome function during replicative senescence.31 Inhibition of AGE formation via blocking sugar attachment to proteins, scavenging the reactive intermediates, or breakdown
of established AGE-induced cross-links, constitutes an attractive therapeutic/preventative target.33 Oleuropein has been demonstrated to inhibit AGE formation and breakdown AGE products through its proteasome enhancing function.31, 33
Phosphatidylserine (PS)
The initial approach to altering the destructive ECM milieu needs to halt the destructive enzymes and end products causing protein fragmentation, misfolding, abnormal cross linkages






