
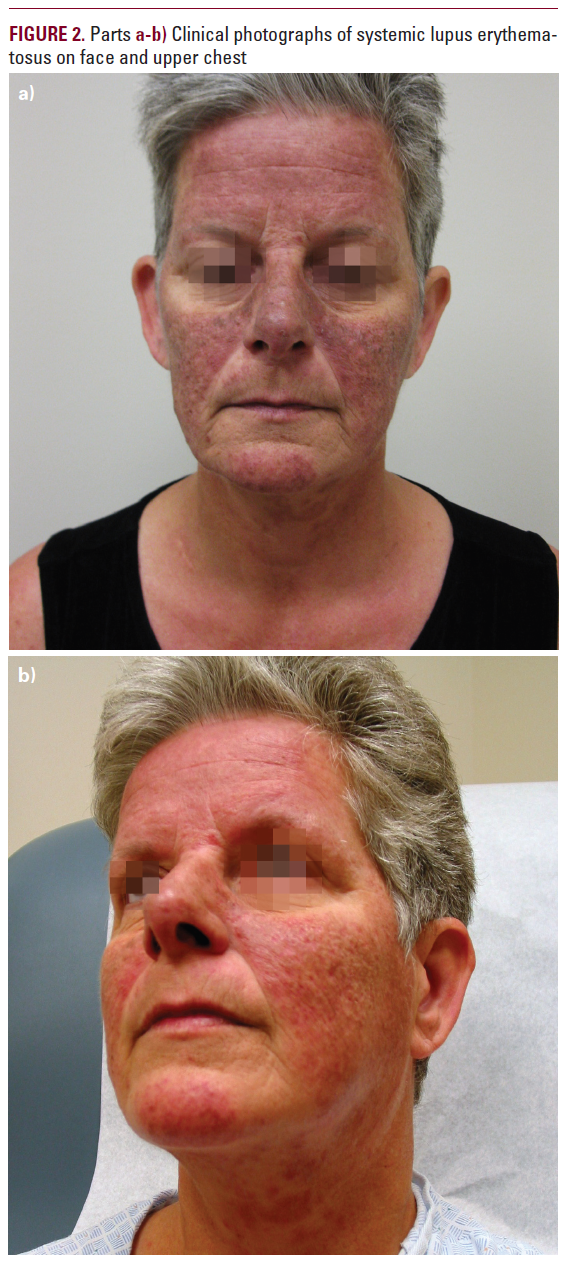
At presentation, the patient had erythematous, crusted
patches, papules and small plaques on most of her forehead,
nose and cheeks and to a lesser degree on her chin, neck,
upper chest and extensor surface of the arms (Figure 2 A-B).
The lesions were non-pruritic, non-tender and not painful.
Biopsies were obtained from the chest and left upper arm
(Figure 3). Both lesions showed hyperkeratosis with focal interface
dermatitis with increased dermal mucin, consistent
with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). An antinuclear antibody
titer drawn that day was positive at 1:1280. An SSA/
RO antibody titer was also positive at 135. SSB/La and Anti-
Jo antibodies were negative. The eruption improved with
application of triamcinolone 0.1% cream and continued to
resolve following cessation of capecitabine.
DISCUSSION
Capecitabine is a novel oral chemotherapeutic agent with
proven efficacy in patients with metastatic breast cancer and
colorectal cancer. The drug is converted to 5'-deoxy-5-fluorocytidine
in the liver and subsequently metabolized in tissue
and tumor first to 5'-deoxy-5-fluorouridime then 5-fluorouracil.
Cutaneous side effects of this drug continue to surface as
its use in cancer management increases. The dose-limiting
side effects most frequently observed with capecitabine are
hyperbilirubinemia, diarrhea, and hand-foot syndrome or
PPE.2 According to Cassidy et al, capecitabine has a safety
profile superior to 5-FU with a lower incidence of diarrhea,
stomatitis, nausea, alopecia, and grade 3 or 4 neutropenia
leading to significantly fewer neutropenic fever/sepsis cases
and fewer hospitalizations.1
Various skin toxicities have been attributed to capecitabine and
reported in the literature. PPE is a common adverse reaction
to capecitabine, occurring in 50% to 68% of patients.3 Rarer
side effects reported include localized skin hyperpigmentation,
onychodystrophy, and stomatitis.4,5 One case of subacute cutaneous
lupus erythematosus has also been reported which
occurred in a patient with preexisting positive ANA titers and a
positive family history of SLE.6






