Artificial Neural Networks Analysis (ANNs)
We transformed the pre-selected clinical variables (Table 1), using the 15 continuous input variables into 30 input variables constructed for each of the variable two classes: high (H) and Low (L) (Table 2).
The semantic map delineates three main profiles, which were marked with three different colors in Figure 1: fast responders in blue, non-responders in yellow and an intermediate profile in red.
Fast-Responders presented at week 0: Lymphocytes_low, P/L_ high, RBC_low, HB_high, WBC_low, Neutrophils_low, Platelets high, AST_high, ALT-high, AST/ALT-high, and clinically PASI_ low, BSA_low, IGA_low.
Non-responders presented at week 0: Neutrophils_high, WBC_ high, RBC_high, ALT/AST_low, AST/ALT_high and clinically BSA_highand IGA_high. Interestingly, non-responders were related to both low and high N/L, therefore in the next step N/L was discarded by TWIST and depicted as a non-representative variable.
TWIST selected 7 of the 30 attributes (Table 2), namely IGA_low, ALT_high, HB_low, WBC_low, Neutrophils_low, PASI_week_0_ low, IGA_high (Table 3).
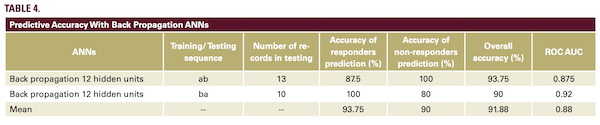
Table 4 shows the predictive accuracy obtained with a back propagation artificial neural networks equipped with 12 hidden units in forecasting the response or non-response to secukinumab according to baseline variables.
DISCUSSION
Using for the first time an ANNs based approach on serological (CBC) and clinical data, we outlined precise response profiles of psoriasis patient fast-responders to the drug secukinumab at 4 weeks. Data available at 4 weeks of treatment in real-life are still scanty and have, to date, not been used to obtain a profiling of responders; also, to date, no biomarkers allowing to predict secukinumab efficacy in long and short periods have been identified.24
Remarkably, in literature CBC data such as neutrophil/ lymphocytes ratio (N/L), mean platelet volume (MPV) or even red blood cell distribution width (RDW) were singularly evaluated in order to predict cardiovascular risk or monitor therapeutic response in psoriatic patients but never as predictors of drug response.25,26
In a multicenter, retrospective real-life study of 107 patients treated with secukinumab, Galluzzo et al reported that after four weeks of treatment 41.2% of patients not naïve to biologics and 60% of patients naive to biologics had achieved PASI >75. A univariate logistic regression analysis suggested that the outcome PASI >75 at 4 weeks could be related to age and prior therapies, which would imply that young naïve patients have a higher potential to achieve PASI >75.5 Remarkably, the presently available literature suggests that the average time to achieve a clinical result could be a significant parameter to predict patients’ compliance and adherence in chronic disorders, particularly in psoriasis.27 In a systematic review, Murage et al concluded that disease severity, reduction of comorbidities, lower out-of-pocket costs, awareness of drug effectiveness, safety, and tolerability were the main determinants for patients’ adherence and drug survival.27
Hence, one can say that identifying real-life responders to secukinumab has so far represented an unmet need. Linear statistics, based on the generalized linear model, proved to be of limited value in predicting the response to a priori drug treatment.28 Likewise, multiple regression demonstrated unsatisfactory results not exceeding 80% of the total variance.29 In contrast, ANNs-based approaches provide a statistical-mathematical method able to determine the existence of a correlation between a series of data and a particular outcome, and when adequately trained, can predict the result against the insertion of data.10 This characteristic makes ANNs ideal for recognizing patterns and solving complex biologic and therapeutic problems.30
Thus, our study used ANNs to depict profiles of fast-responding patients who at week 4 achieved at least PASI >75 using routine blood samples.
The limitation of this study is the small sample size; however, this is a pilot study aimed at investigating the possibility that CBC data may be used to predict patients that would be fast responders to secukinumab at week 4.
Remarkably, in literature CBC data such as neutrophil/ lymphocytes ratio (N/L), mean platelet volume (MPV) or even red blood cell distribution width (RDW) were singularly evaluated in order to predict cardiovascular risk or monitor therapeutic response in psoriatic patients but never as predictors of drug response.25,26
In a multicenter, retrospective real-life study of 107 patients treated with secukinumab, Galluzzo et al reported that after four weeks of treatment 41.2% of patients not naïve to biologics and 60% of patients naive to biologics had achieved PASI >75. A univariate logistic regression analysis suggested that the outcome PASI >75 at 4 weeks could be related to age and prior therapies, which would imply that young naïve patients have a higher potential to achieve PASI >75.5 Remarkably, the presently available literature suggests that the average time to achieve a clinical result could be a significant parameter to predict patients’ compliance and adherence in chronic disorders, particularly in psoriasis.27 In a systematic review, Murage et al concluded that disease severity, reduction of comorbidities, lower out-of-pocket costs, awareness of drug effectiveness, safety, and tolerability were the main determinants for patients’ adherence and drug survival.27
Hence, one can say that identifying real-life responders to secukinumab has so far represented an unmet need. Linear statistics, based on the generalized linear model, proved to be of limited value in predicting the response to a priori drug treatment.28 Likewise, multiple regression demonstrated unsatisfactory results not exceeding 80% of the total variance.29 In contrast, ANNs-based approaches provide a statistical-mathematical method able to determine the existence of a correlation between a series of data and a particular outcome, and when adequately trained, can predict the result against the insertion of data.10 This characteristic makes ANNs ideal for recognizing patterns and solving complex biologic and therapeutic problems.30
Thus, our study used ANNs to depict profiles of fast-responding patients who at week 4 achieved at least PASI >75 using routine blood samples.
The limitation of this study is the small sample size; however, this is a pilot study aimed at investigating the possibility that CBC data may be used to predict patients that would be fast responders to secukinumab at week 4.






