INTRODUCTION
Basal cell carcinomas (BCC) arise from DNA damage to cells of the basal layer of the epidermis and most commonly in areas of the skin exposed to sunlight or ultraviolet radiation. BCC is the most common skin cancer seen in humans with over 4.3 million cases reported in the United States and is responsible for 3-10% of all cancers annually.1,2 We report what we believe to be the first case of this very prevalent skin cancer arising in the nasal vestibule. The lesion was treated with Mohs micrographic surgery and required three stages to obtain histological clearance. Given the location of the tumor, Mohs surgery was chosen due to the procedure’s effectiveness for achieving the highest cure rate with the lowest incidence of tumor recurrence and for preserving as much adjacent healthy tissue as possible.
CASE PRESENTATION
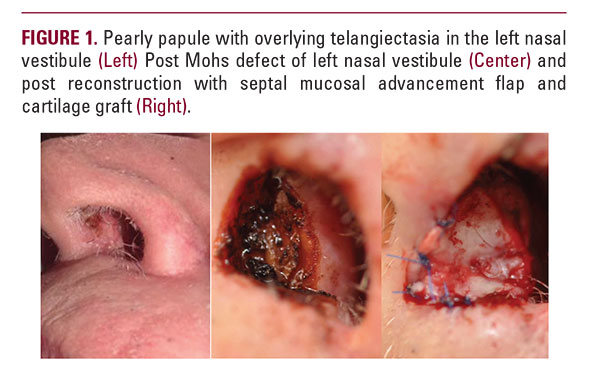
An 81-year-old Caucasian male presented with a lesion in the left anterior nasal vestibule near the base of the septum. The lesion was noted by the patient about 4-6 weeks prior to his presentation and was gradually enlarging. There was no associated pain, bleeding, or drainage. He had a history of several non-melanoma skin cancers in the past, but no history of basal cell carcinomas occurring in uncommon areas. His past medical history revealed chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder that required daily supplemental oxygen via nasal cannula. The tip of the left nasal cannula was next to the newly growing lesion. Additionally, the patient has a previous history of lung cancer that was successfully treated in 2005 and was not active at the time of his presentation of this lesion. The patient reported this lesion because he noticed more diffi culty in breathing than usual. There was no history of prior nasal surgery, trauma to the nose, or usage of metered dose nasal inhalers. Physical examination revealed a 0.8 cm x 0.9 cm somewhat pearly papule with a small area of crust and overlying telangiectasia (Figure 1). Previously, the patient was treated for basal cell carcinomas of the right an-