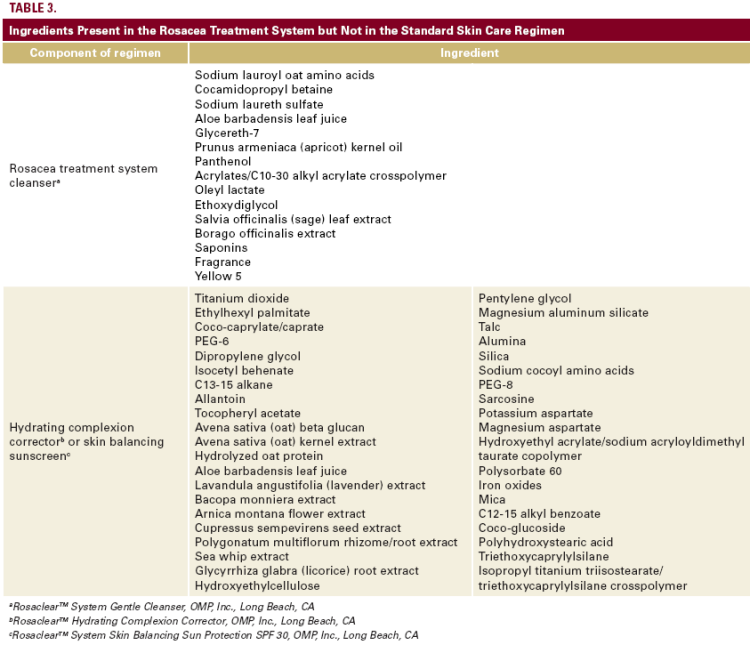
irritated at least sometimes—40 percent with the rosacea treatment
system, 70 percent with the rosacea treatment system minus metronidazole, and 89 percent with metronidazole plus standard care at day 28. This suggests that metronidazole plays some role in enhancing tolerability (reducing the proportion of patients with easily irritated skin from 70% to 40%), but that the ingredients in the rosacea treatment system have an even larger effect (reducing the proportion from 89% to 40%).
Other measures of tolerability (specifically, the effectiveness in reducing dryness, and how comfortable the skin felt after applying
the study products) also showed the superiority of the rosacea treatment system compared to metronidazole 0.75% plus the standard skin care regimen. This further supports the contention that the presence of at least one ingredient in the rosacea treatment system enhances tolerability.
As might be expected, the data presented here also suggest that the rosacea treatment system offers superior efficacy and tolerability to the rosacea treatment system minus the metronidazole, suggesting that the metronidazole component
plays a role in enhancing both these outcomes. The overall results from this study confirm previous findings that the clinical effects achieved with rosacea treatment are dependent on more than a single medication such as metronidazole,
and treatment with such an anti-rosacea medication is improved when used in conjunction with a gentle cleanser, moisturizer, and sunscreen.
While such a multi-pronged approach to treatment brings






